Collagen – you’ve probably encountered the beauty buzzword in all kinds of contexts from skincare to food. As it turns out, the myriad benefits of collagen don’t stop at promoting beautiful and ageless skin – this miracle protein is literally the thing that keeps your body from falling apart into a shapeless blob. So what exactly is collagen?
What is collagen?
Taken from the Greek word kólla meaning glue, collagen is easier imagined as the “glue” that holds our body’s connective tissues together. Making up a whopping third of all the protein in the human body, collagen is the building block that gives strength and structure to our skin, hair, bones, blood vessels, and muscles. It’s the essential protein that we can’t live without – and that we also have to thank for bestowing a smooth and youthful complexion.
Before we go into our best tips for restoring the real-life elixir of youth, first let’s talk about how to differentiate and identify the different types of collagen in the body.
Types of collagen
Found almost everywhere from skin and bones to teeth and hair, collagen is as diverse as it is multifunctional. Different types of collagen can help new cells grow, restore dead skin cells, protect vital organs, strengthen bones and joints, and promote skin elasticity, among other important roles.
While there are around 29 types of collagen that have been identified in the body, here are the 4 main types broken down:
Type I: Accounts for roughly 90% of our body. These collagen fibers are densely packed to provide structure to our skin, bones, tendons, fibrous cartilage, connective tissue, nails and teeth.
Type II: Comprised of loosely packed fibers, and found in elastic cartilage (e.g. outer ear and larynx) and hyaline cartilage (e.g. around bones of free-moving joints).
Type III: The second most abundant collagen in tissues, Type III is made up of meshy fibers that support the framework of muscles, hollow organs (e.g. uterus), and arteries.
Type IV: Mainly responsible for filtration, found within the skin layers.
How do changes in collagen affect how we look?
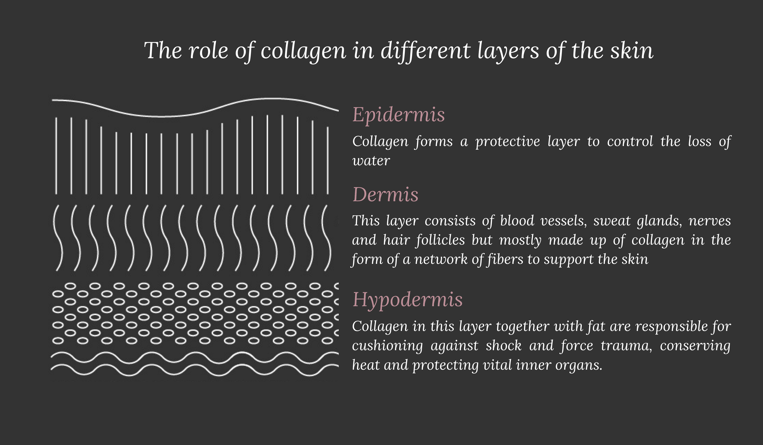
As we age, our bodies produce less and lower quality collagen, leading to the signs of visible aging. According to research, collagen production reduces by a rate of around 1% every year after the age of 25. Sun damage, environmental pollutants, smoking, and increased blood sugar are all contributing factors towards worsening collagen depletion, making it much harder for skin to “bounce back” like it did in your early twenties.
While it’s all part of the natural aging process, collagen loss – along with environmental stressors, gravity and everyday facial expressions – can cause facial lines to appear, skin to sag, and the jawline to become less defined over time.
How to restore collagen production
Good news – more and more scientific evidence is showing that aging and damaged skin can be rejuvenated by restoring collagen with antiaging technologies, devices, and ingredients. There are now so many innovative ways to use, deliver, and replenish collagen to retain that youthful glow.
Here are some of our favorite ways to keep skin young and supple using the benefits of collagen:
Collagen creams: While unable to restore cumulative collagen loss, collagen creams are effective for hydrating and keeping skin plump – essential for staving off premature aging. Paired with supercharging ingredients like hyaluronic acid and vitamin C, collagen creams can help to maintain and improve complexion.
Collagen mask: With nanotechnology, it is now possible for active ingredients to be penetrated deeper into the skin
Collagen injection: Collagen injections are a cosmetic procedure that directly replenishes the skin’s natural collagen with a replacement of bovine (cow) or human collagen. However, just like natural collagen, the collagen replacements will eventually deplete over time and will need topping up two to four times a year.
Natural dietary collagen: Considered the most effective option, collagen can be obtained naturally through the consumption of collagen-rich foods like bone broths, pork or chicken skin, egg whites, fish, and food that contains gelatin. Other types of nutrient-rich food that might not contain collagen but aid in the body’s production of collagen include aloe vera, oyster, ginseng, and spirulina.
Collagen supplements: If you find it hard to follow a collagen-rich diet, then there are oral collagen supplements you can take instead. Hydrolyzed collagen (aka collagen peptides) is collagen that has been broken down to make it easier for your body to absorb. The resulting collagen peptides are bioactive, meaning once absorbed into the bloodstream, they can trigger a number of functions from stimulating fibroblasts in the skin to produce more hyaluronic acid to help provide structural support for skin and hair. Taking skincare gummies is a guilt-free and pleasurable way to treat your skin.
Microneedling: At home, a derma-roller can be used to create pinprick micro-wounds with hundreds of tiny needles on a wheel. This popular beauty treatment triggers the skin’s natural wound healing process, boosting collagen growth, reducing the appearance of fine lines, and improving overall complexion.
Red light therapy (RLT): Red low-level wavelengths of light are used to cure everything from acne and inflammation to fine lines. According to a 2014 study that sought to determine the efficacy of red light and near-infrared light, the results were promising: RLT users experienced vastly improved skin complexions and boosted collagen levels over time. The best part is, this gentle and non-invasive treatment is suitable for all skin types.
While it’s easy to focus on fixing what you can see at face value, beauty isn’t just skin deep. Good skin is an indicator of how the rest of the body is feeling, and after a year dominated by the COVID pandemic, we’re learning more than ever that health is indeed wealth. Boosting collagen not only improves your skin, but other key bodily functions that are crucial for good health in the long run!
.png?width=180&height=80&name=imgpsh_fullsize_anim%20(1).png)

